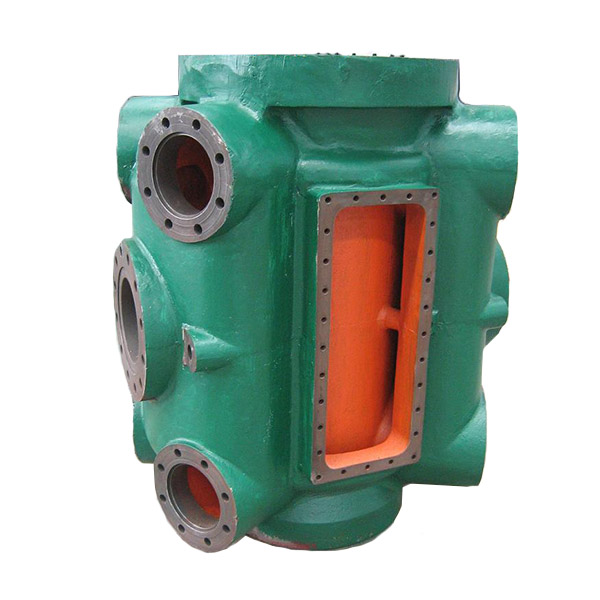
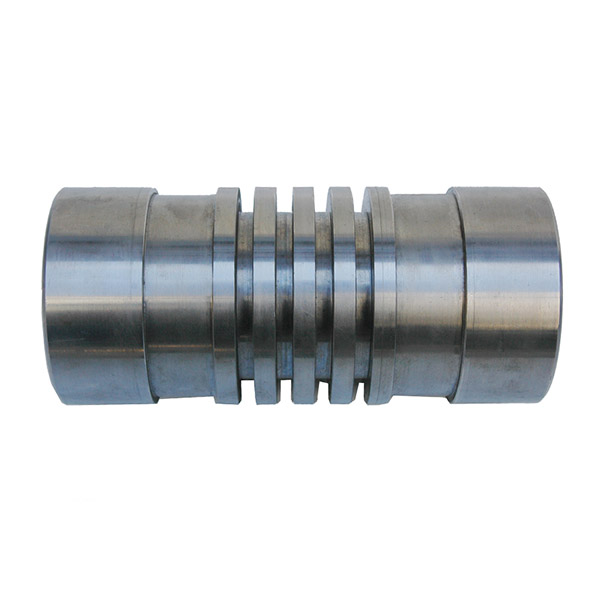
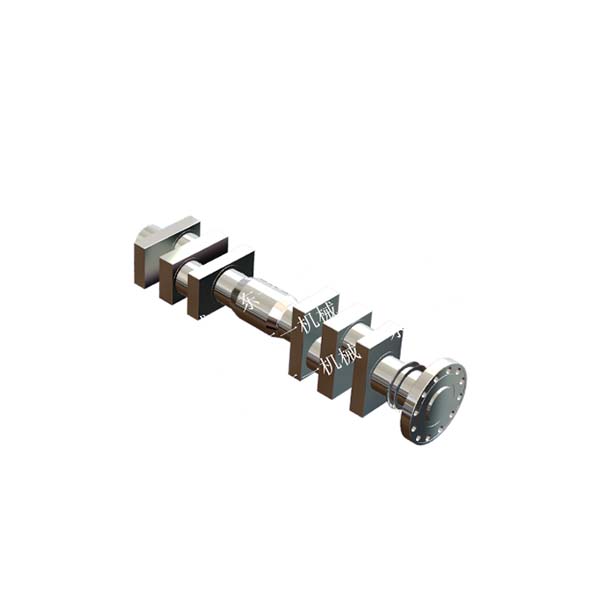
A piston compressor, also known as a reciprocating compressor, consists of several key components that work together to compress air or gas. Here are the main parts and their functions:
1. Cylinder
Function: The cylinder is the chamber where the piston moves back and forth, compressing the gas.
Material: Typically made from cast iron, steel, or aluminum for durability and heat resistance.
2. Piston
Function: The piston moves within the cylinder, creating pressure changes that compress the gas.
Material: Often made from aluminum or cast iron, chosen for their strength and wear resistance.
3. Piston Rings
Function: These rings provide a seal between the piston and the cylinder wall, preventing gas leakage and maintaining compression.
Material: Usually made from cast iron or steel, sometimes coated with materials like chrome or molybdenum for enhanced durability.
4. Crankshaft
Function: Converts the rotational motion from the motor into the reciprocating motion of the piston.
Material: Typically made from forged steel for strength and durability.
5. Connecting Rod
Function: Connects the piston to the crankshaft, transferring the motion from the crankshaft to the piston.
Material: Usually made from steel or aluminum.
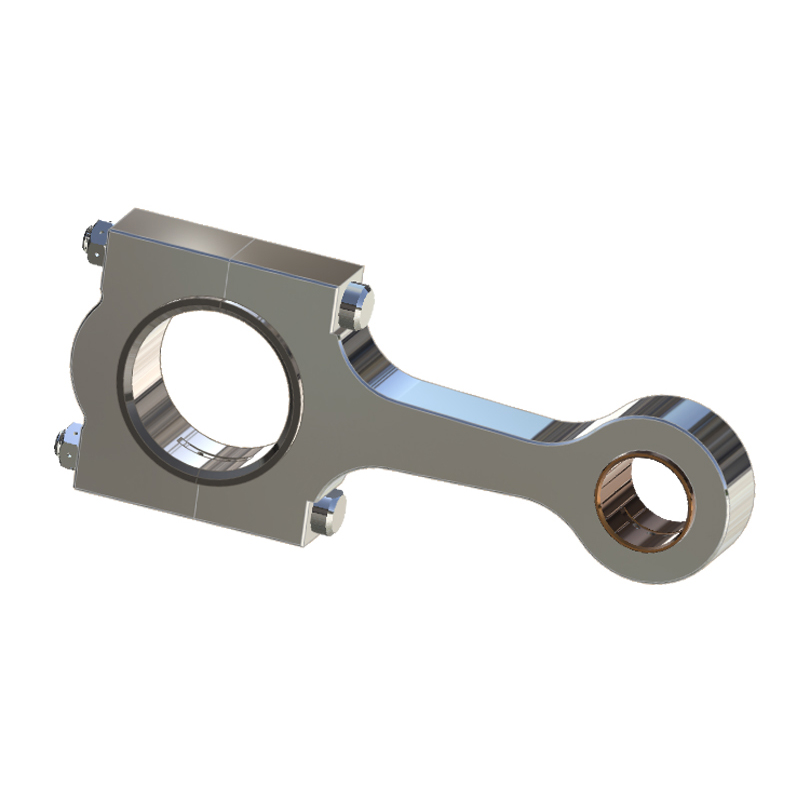

6. Valves
Function: Control the flow of gas into and out of the cylinder. There are typically two types of valves:
Intake (Suction) Valve: Allows gas to enter the cylinder during the intake stroke.

Discharge (Exhaust) Valve: Allows compressed gas to exit the cylinder during the compression stroke.
Material: Often made from high-strength steel or stainless steel for durability and resistance to wear.
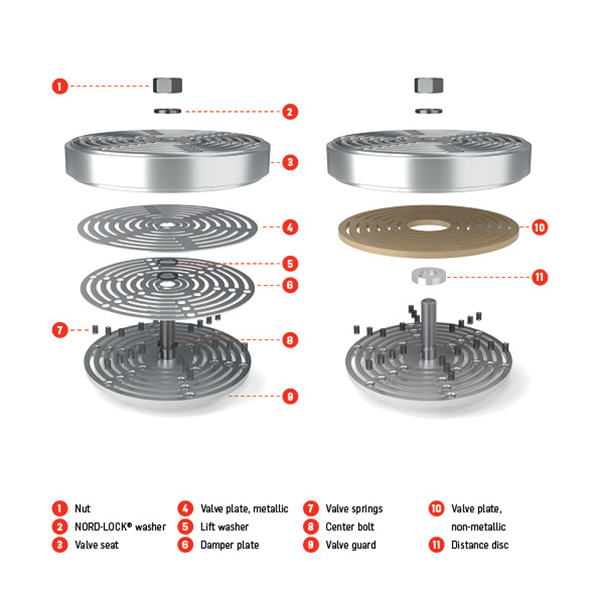
7. Valve Plate
Function: Houses the intake and discharge valves, controlling their operation.
Material: Typically made from steel or aluminum.
8. Crankcase
Function: Encases the crankshaft and other moving parts, providing support and housing for lubricating oil.
Material: Made from cast iron, aluminum, or steel.
9. Cylinder Head
Function: Seals the end of the cylinder and contains the valves and valve plate.
Material: Typically made from cast iron or aluminum.
10. Cooling System
Function: Removes excess heat generated during compression to prevent overheating. This can be an air cooling system (using fins and fans) or a water cooling system (using water jackets and radiators).
Components:
Fins and Fans (for air cooling)
Water Jackets and Radiators (for water cooling)
11. Lubrication System
Function: Reduces friction between moving parts and removes heat. It can be splash lubrication or forced lubrication.
Components:
Oil Pump (for forced lubrication)
Oil Reservoir or Sump
12. Flywheel
Function: Helps maintain a steady rotational speed of the crankshaft and provides momentum to aid in the smooth operation of the compressor.
Material: Typically made from cast iron or steel.
13. Gaskets and Seals
Function: Prevent leaks of gas or oil between different components and ensure proper sealing.
Material: Made from various materials such as rubber, silicone, or composite materials depending on the application.
14. Motor/Engine
Function: Provides the mechanical power needed to drive the crankshaft. This can be an electric motor or an internal combustion engine.
Types:
Electric Motor: Common in stationary compressors.
Internal Combustion Engine: Often used in portable or remote compressors.
Summary
Each part of a piston compressor plays a vital role in its operation, from the cylinder where compression occurs to the motor that drives the entire process. Understanding these components and their functions helps in maintaining and troubleshooting the compressor, ensuring efficient and reliable performance.



